Wood pellets are a type of biomass fuel made from compressed organic materials, typically sawdust, wood shavings, or other wood waste products. These pellets are small, cylindrical in shape, and have a uniform size, usually about 6–8 mm in diameter and 10–30 mm in length. Wood pellets are used as an eco-friendly fuel source in various heating systems, power generation, and industrial processes.
KV VIET NAM JOINT STOCK COMPANY is one of leading manufactures Wood pellet in Vietnam
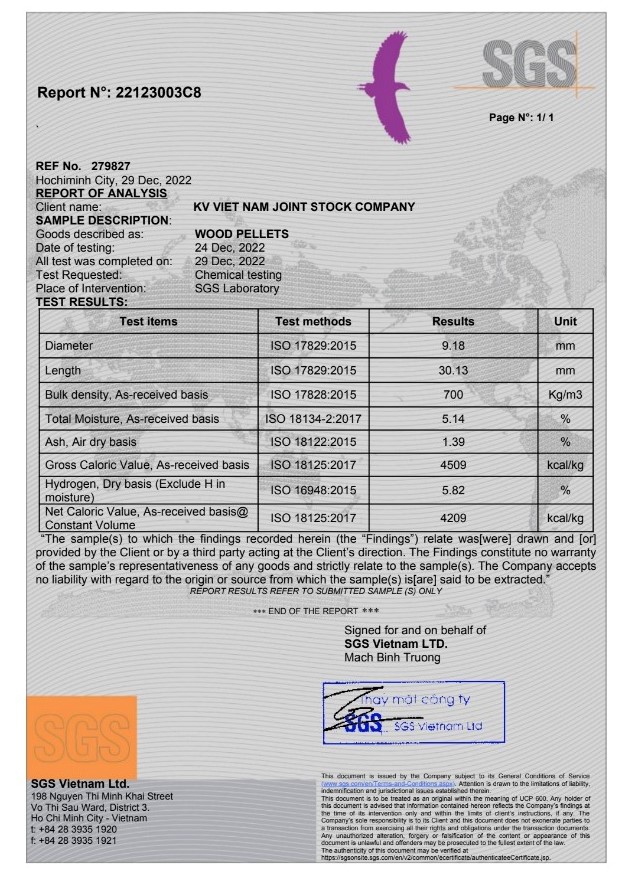
- Application: Industrial
- Diameter: <9mm
- Length: 10-40mm
- Moisture (%): <10
- Ash Content (%): <3
- Calory (J): 4500
- Supply Ability: 2000Ton/Month
Wood pellet from Vietnam
Wood pellets from Vietnam have become a significant part of the global biomass energy market, particularly in response to increasing demand for renewable energy sources. Vietnam is now one of the world’s top exporters of wood pellets, with large shipments going to countries like South Korea, Japan, and European nations. These wood pellets are made primarily from wood waste such as sawdust, wood shavings, and wood chips, sourced from Vietnam’s abundant timber and wood-processing industries.
Key Features of Wood Pellets from Vietnam:
1. Raw Material Sources:
- Timber By-Products: Vietnamese wood pellets are mainly produced from by-products of the furniture, timber, and paper industries. This includes sawdust, wood chips, and wood shavings, which would otherwise be discarded or burned.
- Wood Types: The most common wood used for pellet production in Vietnam includes acacia, eucalyptus, rubberwood, and other plantation-grown species.
- Sustainability Concerns: Ensuring that wood pellets are sourced from sustainably managed forests is a growing priority. Some producers are seeking FSC (Forest Stewardship Council) certification to meet the sustainability criteria of international buyers.
2. Key Export Markets:
- South Korea: Vietnam is a major supplier of wood pellets to South Korea, where they are used in power plants for co-firing with coal. South Korea is aiming to reduce its reliance on fossil fuels, and wood pellets play a key role in their renewable energy strategy.
- Japan: Japan is another major buyer of Vietnamese wood pellets, using them in biomass power plants. The Japanese government has implemented policies that encourage the use of biomass as part of its renewable energy transition.
- Europe: Several European countries, such as the UK, the Netherlands, and Belgium, import wood pellets from Vietnam to meet their renewable energy targets. European demand is driven by a push for carbon-neutral energy sources.
3. Quality Standards:
- Vietnamese wood pellets are generally manufactured to meet international standards, including ENplus certification, which ensures the pellets are of high quality in terms of dimensions, moisture content, ash content, and energy value.
- Typical Vietnamese wood pellets have the following characteristics:
- Diameter: 8-9 mm
- Length: 10-40 mm
- Moisture Content: <10%
- Ash Content: <3%
- Calorific Value: 4,000-4,800 kcal/kg
4. Production Capacity:
- Vietnam has over 200 wood pellet production facilities with significant output capacity, allowing the country to supply large volumes of pellets to the global market. Annual export volumes exceed 3 million tons, and this figure is expected to rise as global demand for biomass energy increases.
- Production is concentrated in the southern and central regions of Vietnam, close to key export hubs like Ho Chi Minh City and Da Nang.
5. Competitive Advantages:
- Cost-Effective Production: Vietnam benefits from low production costs, particularly in terms of raw material availability (wood waste from its large timber and furniture industries) and labor.
- Strategic Location: Vietnam’s proximity to key markets in Asia (especially South Korea and Japan) offers advantages in terms of lower transportation costs and faster delivery times compared to other major wood pellet suppliers like North America and Europe.
- Favorable Trade Agreements: Vietnam’s participation in trade agreements such as the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) and Vietnam-EU Free Trade Agreement (EVFTA) reduces tariffs and facilitates easier access to global markets.
6. Environmental and Market Challenges:
- Sustainability and Certification: As global attention to climate change and sustainable practices increases, Vietnamese exporters are being encouraged to adopt sustainable forest management and certification schemes like FSC.
- Raw Material Supply Pressure: The rising demand for wood pellets has led to concerns about the long-term sustainability of raw material supplies. Vietnam needs to ensure its forests and plantations are managed sustainably to avoid deforestation and depletion of resources.
- Price Volatility: The price of wood pellets can fluctuate based on energy market trends and changes in demand from key importing countries, which can impact profitability for Vietnamese producers.
Future Outlook:
Vietnam’s wood pellet industry is expected to continue growing, driven by the increasing global shift towards renewable energy and decarbonization. The country’s strong timber industry, low production costs, and strategic location make it well-positioned to capitalize on the demand for biomass energy.
However, in order to maintain its competitive edge, Vietnam will need to focus on:
- Enhancing Sustainability Practices: Securing certifications like FSC to meet the requirements of environmentally conscious buyers.
- Improving Production Efficiency: Investing in new technologies to improve pellet quality and production capacity.
- Expanding into New Markets: Beyond South Korea and Japan, Vietnam has potential opportunities to grow its exports to other regions, especially Europe and North America, as the demand for renewable energy continues to rise.
With its current advantages and the global push for cleaner energy sources, Vietnam is set to remain a key player in the wood pellet market.



Orther product:
